Write a java program to validate a PAN Card number. A PAN card number is said to be valid when it starts with 5 uppercase letters 4 digits and Followed by single upper case letter. A Valid PAN have only 10 letters.
For example: a pan card number AMEPJ2585B is valid where as AM525LDKF is invalid.
Given below is the java program which makes use of regular expressions to validate the PAN number.
ValidPan.java
For example: a pan card number AMEPJ2585B is valid where as AM525LDKF is invalid.
Given below is the java program which makes use of regular expressions to validate the PAN number.
ValidPan.java
import java.util.*; class ValidPAN { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner scn=new Scanner(System.in); int t=scn.nextInt(); String s[]=new String[t]; boolean output[]=new boolean[t]; for(int i=0; i<s.length;i++) { s[i]=scn.next(); boolean ss=s[i].matches("[A-Z]{5}\\d{4}[A-Z]{1}"); output[i]=ss; } for(boolean b:output) { System.out.println(b); } } }
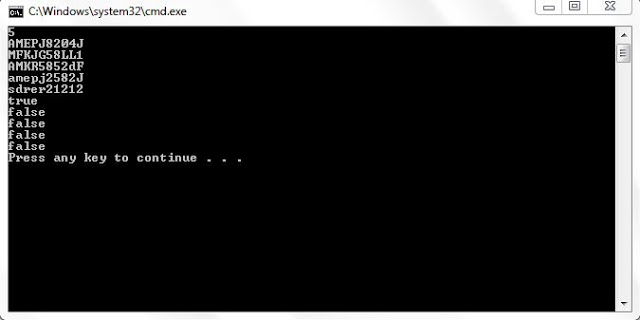
Sample Output:



![How to access the private method of a class outside of the class in Java. [Reflection]](http://3.bp.blogspot.com/-Yw8BIuvwoSQ/VsjkCIMoltI/AAAAAAAAC4c/s55PW6xEKn0/s1600-r/nth.png)
![Write a Java program to print the following pattern. [Interview Question]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEhjW-EAGzLrrcyLB1t-wL2TPMj8EOAvS6xgYWypm14D0II20GGoVIPpZmw7Fc5unqP06gsUc2CYIIJIKYWBmJG8o8w-q-ffbE08U4kJEWiyuALq5i4mVm75EzRhALaWvygxK5hfZSYQIfAm/s1600/Triangle.JPG)
![[Webdriver] Selenium test script to scroll and print all items name from a web page.](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEgWuXvsPDNmLDLYoiqIxSXouZJFCQg84g5f11UPrij9o6SqZPgho7beatQQlO9Z58MMSLNDNCfJQR99fqUogL6ZFOay8HNKdIQbrcl4NKK3oao7pBtQBlDE6qpImsIQ220Wq3f4fzN6swyB/s1600/1.JPG)







